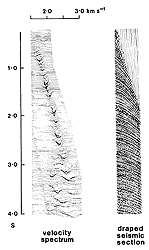
For each CMP gather, the velocity analysis is done at many times. A
common method of displaying this work can be seen in the example to the
right (click the image for a larger version). The velocity
spectrum defines
the stacking velocity as a function of reflection time. The energy (cross-power
) function used to define the stacking velocity is calculated for a large number
of narrow time windows along a seismic section. The velocity spectrum is typically
displayed alongside the draped section. In the example shown here, stacking
velocities for all times less than about 3 seconds are reasonably clear. Beyond
3 seconds there are multiple peaks that are caused by overlapping hyperbolic
trajectories. The low velocity arrivals are due to multiple reflections in
the near surface. They arrive at the same time as the reflection events from
deep horizons.
A stacking velocity is defined for each time sample. The normal moveout correction
and stacking can be carried out by summing along a different hyperbola for
each time on the seismogram. Equivalently, the CMP gather may first be NMO
corrected and then stacked. Both approaches are done in practise.
© UBC EOS, D.W. Oldenburg and F. Jones |

